Absolute Value
Pronunciation: /ˈæb.səˌlut ˈvæl.ju/ ExplainAbbreviation: abs
The absolute value of a number is the distance of that number from zero. For real numbers, the absolute value is also called the magnitude. In British English, absolute value is called modulus. Absolute value is written using vertical lines surrounding the values: '|x|' means the absolute value of x. In computers and calculators, absolute value is written as a function, usually abs(a) which means, 'Absolute value of a'.
The absolute value of x is written |x|. The absolute value of -7 is written |-7|.
|
Click on the blue point and drag it to change the figure. The blue point labeled a represents a real number. The red point labeled |a| represents the absolute value of a. What happens to the red point if a is positive? What happens to the red point if a is negative? |
| Manipulative 1 - Absolute Value Created with GeoGebra. |
Note that absolute value is always positive or zero. It can never be negative.
How to find the absolute value of a real number
To find the absolute value of a real number:
- If the number is positive or zero, use the number without changing it.
- If the number is negative, change the number to a positive.
Demonstration
Click on the blue and yellow boxes below to see the next slide.
- Find the absolute value of a positive number.

- Find the absolute value of a negative number.

Formula
Absolute value can be defined using the distance formula:
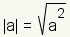
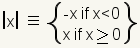
How to Graph a Linear Absolute Value Equation
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|
How to find the absolute value of a complex number
|
The absolute value of a complex number is the distance of that number from the
origin (0,0). The distance formula
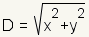 is used to find the absolute value of a complex number. See manipulative 3.
is used to find the absolute value of a complex number. See manipulative 3.
MagnitudeIn advanced mathematics, when referring to the absolute value of a complex number,
the term magnitude is used more often. The word
magnitude has a more general meaning.
Vectors,
which do not have a distance, have a magnitude. The magnitude of a vector is
strength of the force represented by a vector. The distance formula also generalizes
to a formula for magnitude of a vector. For vector
<x,y>,
the magnitude is | |||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- McAdams, David E.. All Math Words Dictionary, absolute value. 2nd Classroom edition 20150108-4799968. pg 9. Life is a Story Problem LLC. January 8, 2015. Buy the book
Educator Resources
- McAdams, David E.. Absolute Value Classroom Demonstrator. allmathwords.org. 12/23/2009. http://allmathwords.org/en/a/absolutevalue_cd.html.
Cite this article as:
McAdams, David E. Absolute Value. 4/12/2019. All Math Words Encyclopedia. Life is a Story Problem LLC. http://www.allmathwords.org/en/a/absolutevalue.html.Image Credits
- All images and manipulatives are by David McAdams unless otherwise stated. All images by David McAdams are Copyright © Life is a Story Problem LLC and are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Revision History
4/12/2019: Changed equations and expressions to new format. (McAdams, David E.)12/21/2018: Adjusted text to support How To index. Expanded discussion of absolute value of a complex number. (McAdams, David E.)
12/21/2018: Reviewed and corrected IPA pronunication. (McAdams, David E.)
6/12/2018: Removed broken links, changed Geogebra links to work with Geogebra 5, updated license, implemented new markup. (McAdams, David E.)
3/12/2011: Increased font size on manipulative graphics. Added label 'B=abs(A)' to manipulative 1. Changed Figure 2 to Manipulative 2 and Manipulative 2 to Manipulative 3. Change section titled 'Graph' to section titled 'Graphing a Linear Absolute Value Equation' and added how to table. (McAdams, David E.)
9/30/2010: Added function notation and additional text on magnitude. (McAdams, David E.)
12/24/2009: Added "References". (McAdams, David E.)
12/9/2009: Added British English Modulus. (McAdams, David E.)
11/19/2008: Added absolute value of a complex number. (McAdams, David E.)
10/5/2008: Expanded 'More Information'. (McAdams, David E.)
9/16/2008: Changed figure 1 to manipulative. (McAdams, David E.)
5/29/2008: Added abs. (McAdams, David E.)
3/3/2008: Added graph and function notation. (McAdams, David E.)
7/12/2007: Initial version. (McAdams, David E.)
- Navigation
- Home
- Contents
-
# A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z - Teacher Aids
- Classroom Demos
- How To
- LIASP
- LIASP Home
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Donate to LIASP
- Help build this site
- About LIASP
- Contact LIASP
All Math Words Encyclopedia is a service of
Life is a Story Problem LLC.
Copyright © 2018 Life is a Story Problem LLC. All rights reserved.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
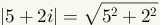
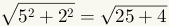
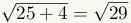

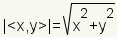 .
.